marine litter
Type of resources
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
-
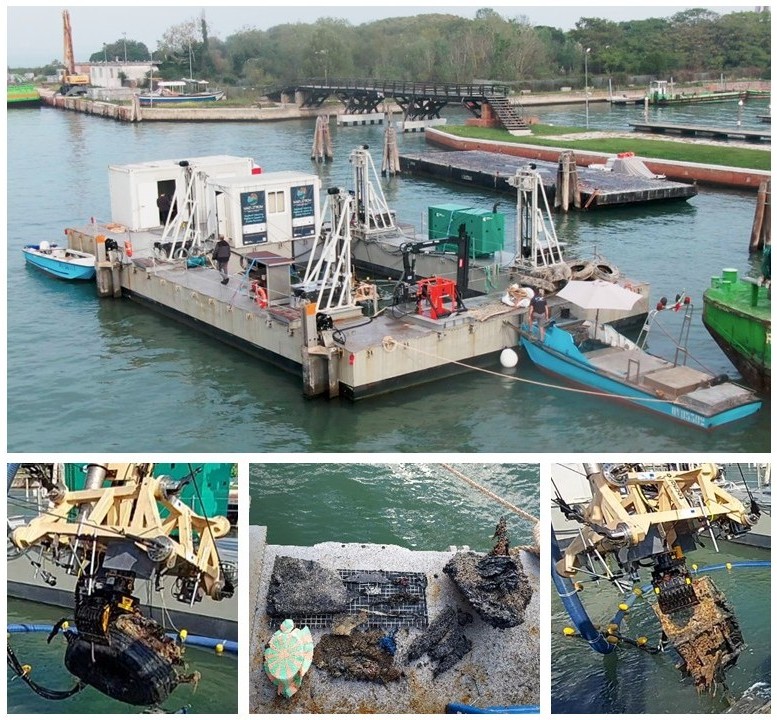

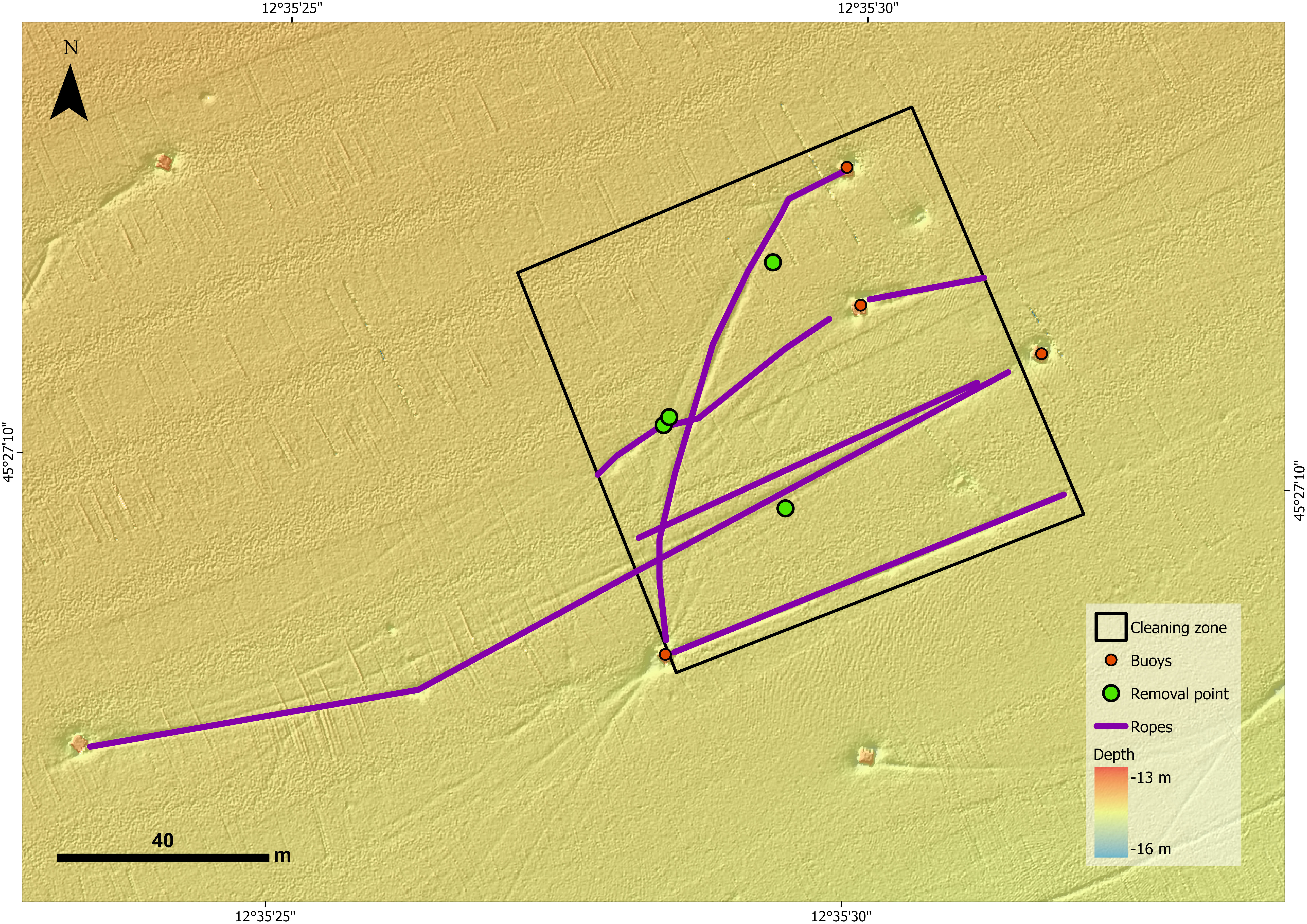
MAELSTROM (Smart Technology for Marine Litter Sustainable Removal and Management) is a Horizon 2020 (H2020) project co-funded by the European Commission, bringing together 14 partners, including research centers, recycling companies, marine scientists, and robotics experts, from eight European countries. The project seeks to reduce the environmental impact of marine litter (ML) on coastal ecosystems by identifying accumulation hotspots, intercepting floating river waste, and removing plastic-based debris from the seabed to prevent its breakdown into microplastics (MPs). At the core of MAELSTROM’s innovative solution is an advanced robotic seabed cleaning platform, developed collaboratively by TECNALIA, CNRS-LIRMM, and "Servizi Tecnici." This floating structure serves as a base station for the cleaning robot, deploying it via cables and winches while integrating a sophisticated suite of underwater sensors to detect, identify, and manage marine litter. The platform supports two key tools: a dredge for collecting smaller debris and a gripper for retrieving larger items, such as tires, boat fragments, and fishing nets. Designed to function as an adaptable and sustainable system, this platform exemplifies cutting-edge technology for marine litter removal and management.
-
Shape files con il marine litter identificato mediante sia mediante riconoscimento manuale sia mediante l'utilizzo di un workflow in ArcGis applicato alla batimetria di input
-
Shape files con il marine litter identificato mediante sia mediante riconoscimento manuale sia mediante l'utilizzo di un workflow in ArcGis applicato alla batimetria di input
-
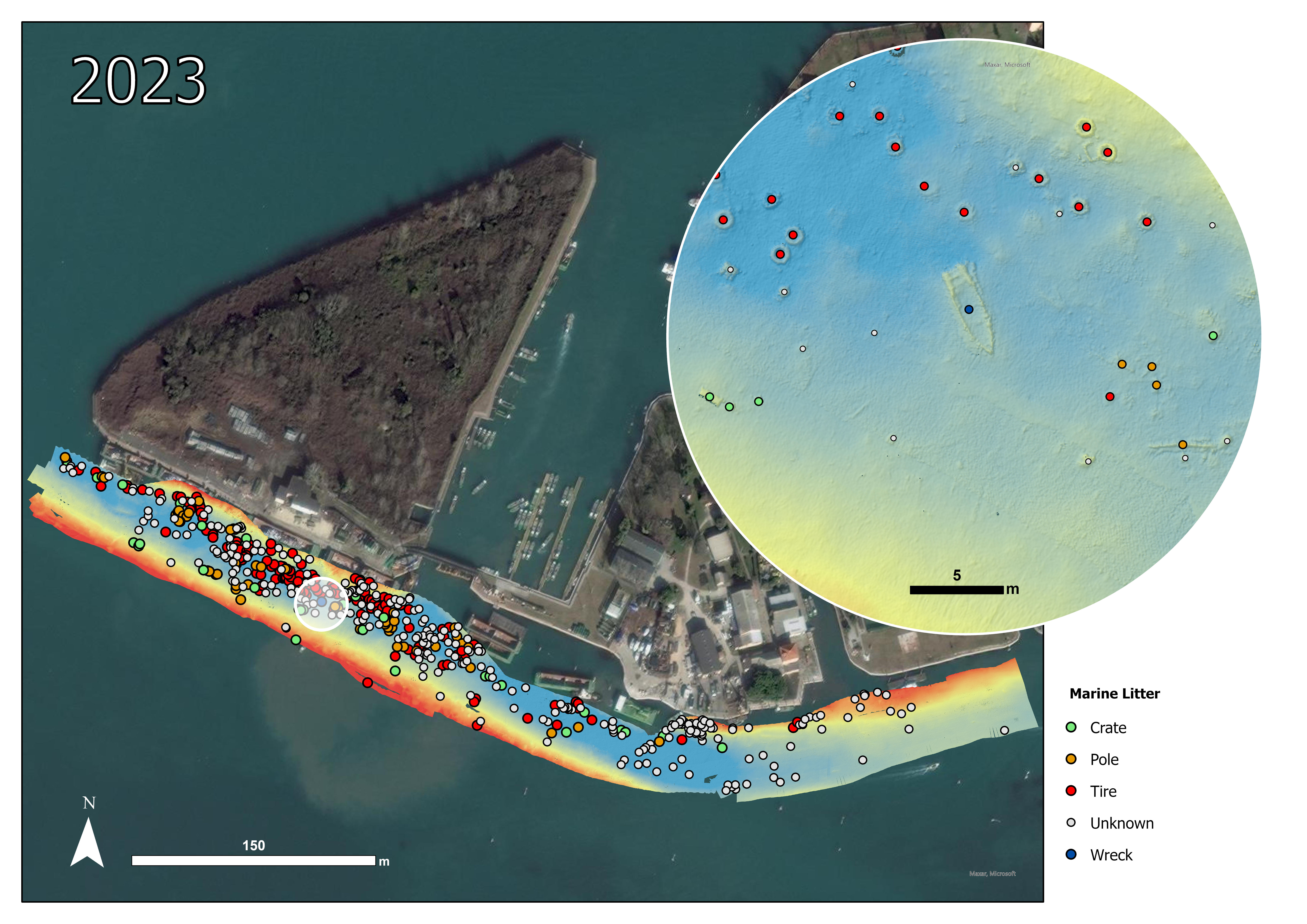
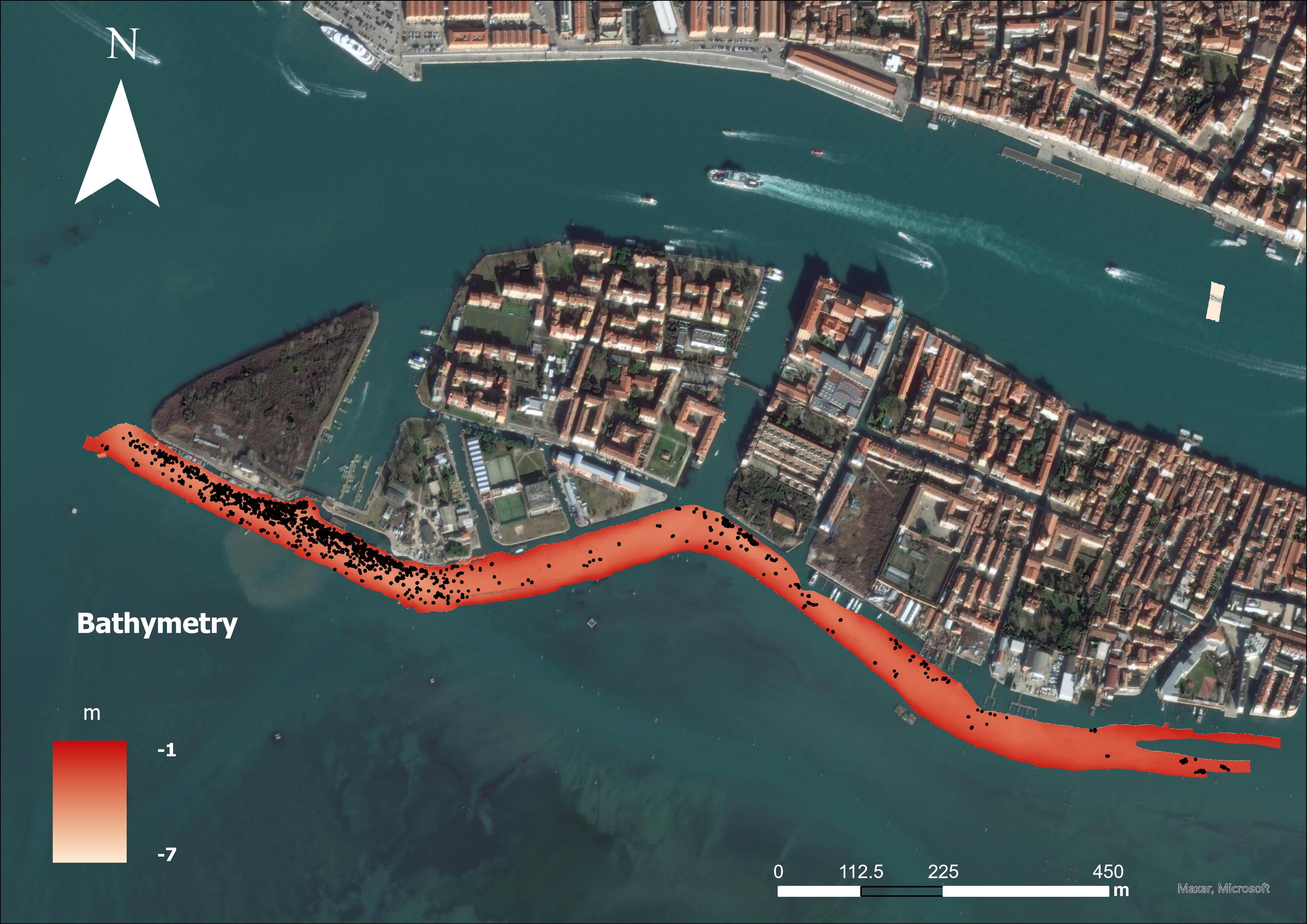
For this project, two study areas were selected and both are characterized by the presence of marine litter that has accumulated over time: a lagoon area (Sacca Fisola) and a coastal area, the latter located on an abandoned mussel farm.The lagoon site of Sacca Fisola is situated in an area where waste accumulates in substantial quantities. Consequently, the channel's seabed is marked by a significant presence of waste. Some of these waste items are buried beneath layers of sediment, while many others remain visible on the surface and can be identified using the bathymetric map generated from MultiBeam EchoSounder (MBES) data.
-
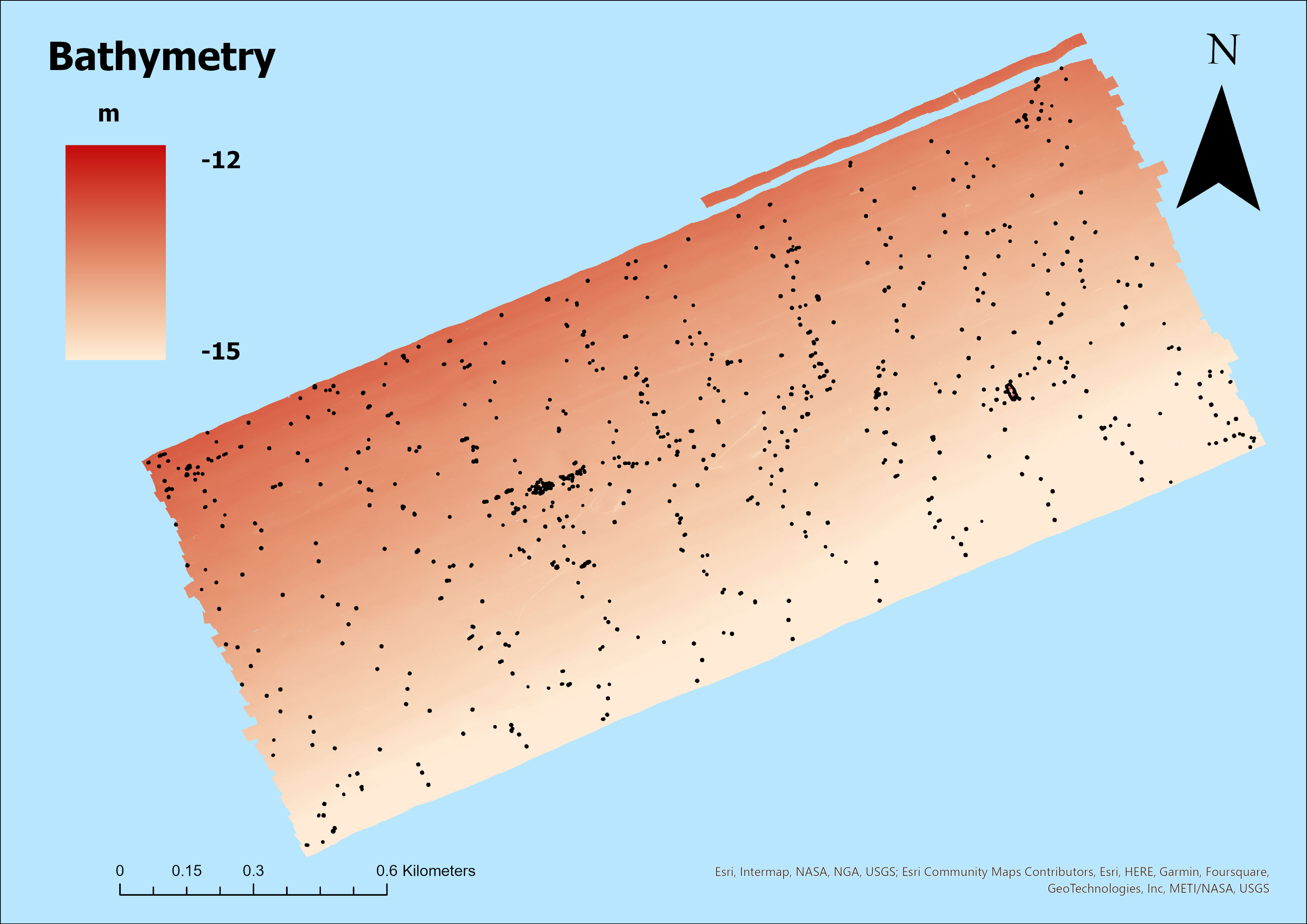
For this project, two study areas were selected and both are characterized by the presence of marine litter that has accumulated over time: a lagoon area (Sacca Fisola) and a coastal area, the latter located on an abandoned mussel farm. The abandoned mussel farm is situated across of the mouth of the river Sile, about 1.7 nautical miles from the coast. It covers a total area of 1960000 sqm with an average depth of 14 m. Mussel farm encloses a sub area called Experimental Field, used in the past for research activities. The examination of bathymetric data facilitated the acquisition of a precise estimation regarding the presence of objects suspended within the water column and resting on the seabed. This evaluation uncovered valuable insights into the underwater conditions and object types, thus enhancing our comprehension of the marine environment in the regions examined.
-
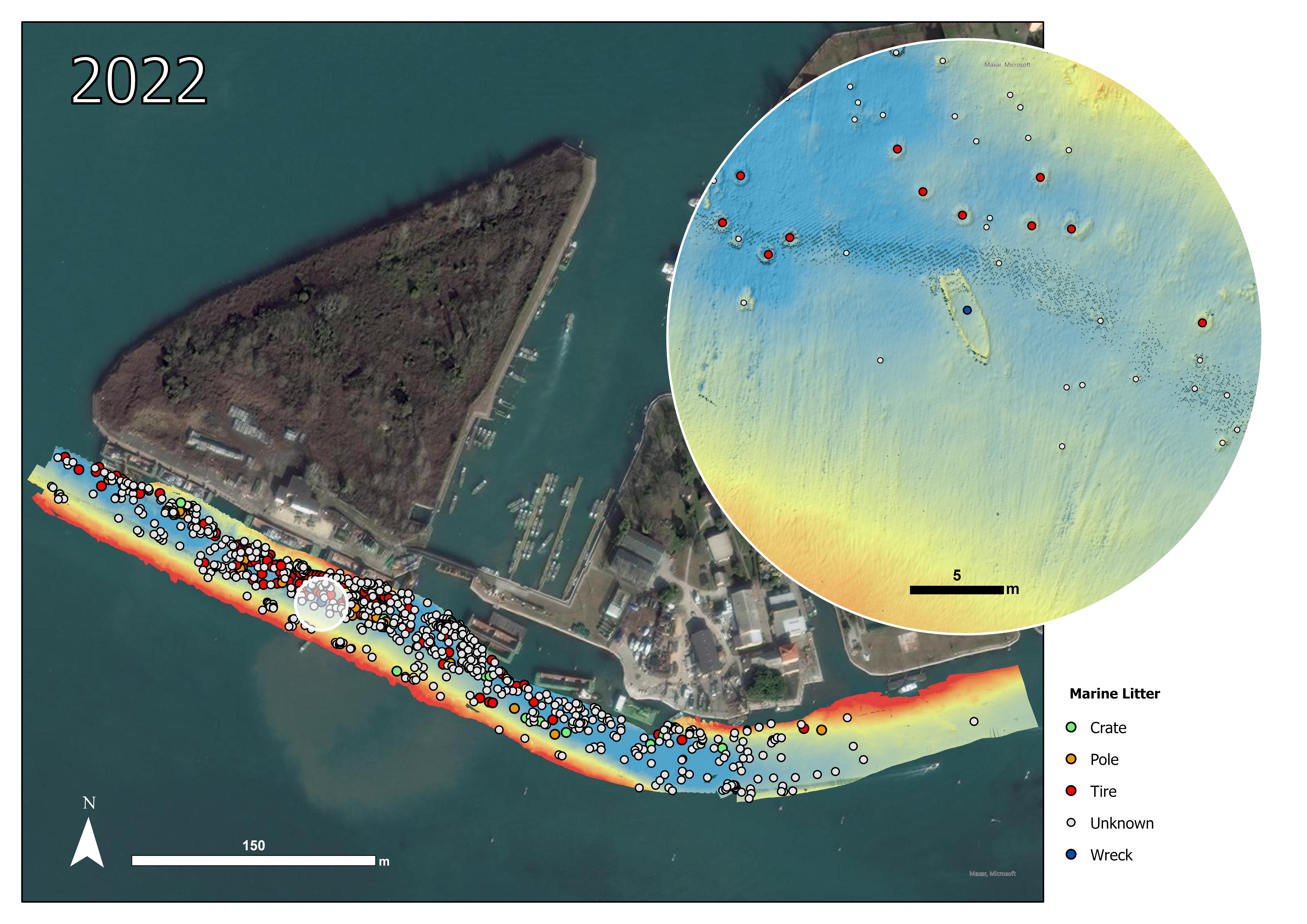
For this project, two study areas were selected and both are characterized by the presence of marine litter that has accumulated over time: a lagoon area (Sacca Fisola) and a coastal area, the latter located on an abandoned mussel farm.The lagoon site of Sacca Fisola is situated in an area where waste accumulates in substantial quantities. Consequently, the channel's seabed is marked by a significant presence of waste. Some of these waste items are buried beneath layers of sediment, while many others remain visible on the surface and can be identified using the bathymetric map generated from MultiBeam EchoSounder (MBES) data.
-

MAELSTROM (Smart Technology for Marine Litter Sustainable Removal and Management) is a Horizon 2020 (H2020) project co-funded by the European Commission, bringing together 14 partners, including research centers, recycling companies, marine scientists, and robotics experts, from eight European countries. The project seeks to reduce the environmental impact of marine litter (ML) on coastal ecosystems by identifying accumulation hotspots, intercepting floating river waste, and removing plastic-based debris from the seabed to prevent its breakdown into microplastics (MPs). At the core of MAELSTROM’s innovative solution is an advanced robotic seabed cleaning platform, developed collaboratively by TECNALIA, CNRS-LIRMM, and "Servizi Tecnici." This floating structure serves as a base station for the cleaning robot, deploying it via cables and winches while integrating a sophisticated suite of underwater sensors to detect, identify, and manage marine litter. The platform supports two key tools: a dredge for collecting smaller debris and a gripper for retrieving larger items, such as tires, boat fragments, and fishing nets. Designed to function as an adaptable and sustainable system, this platform exemplifies cutting-edge technology for marine litter removal and management.
-
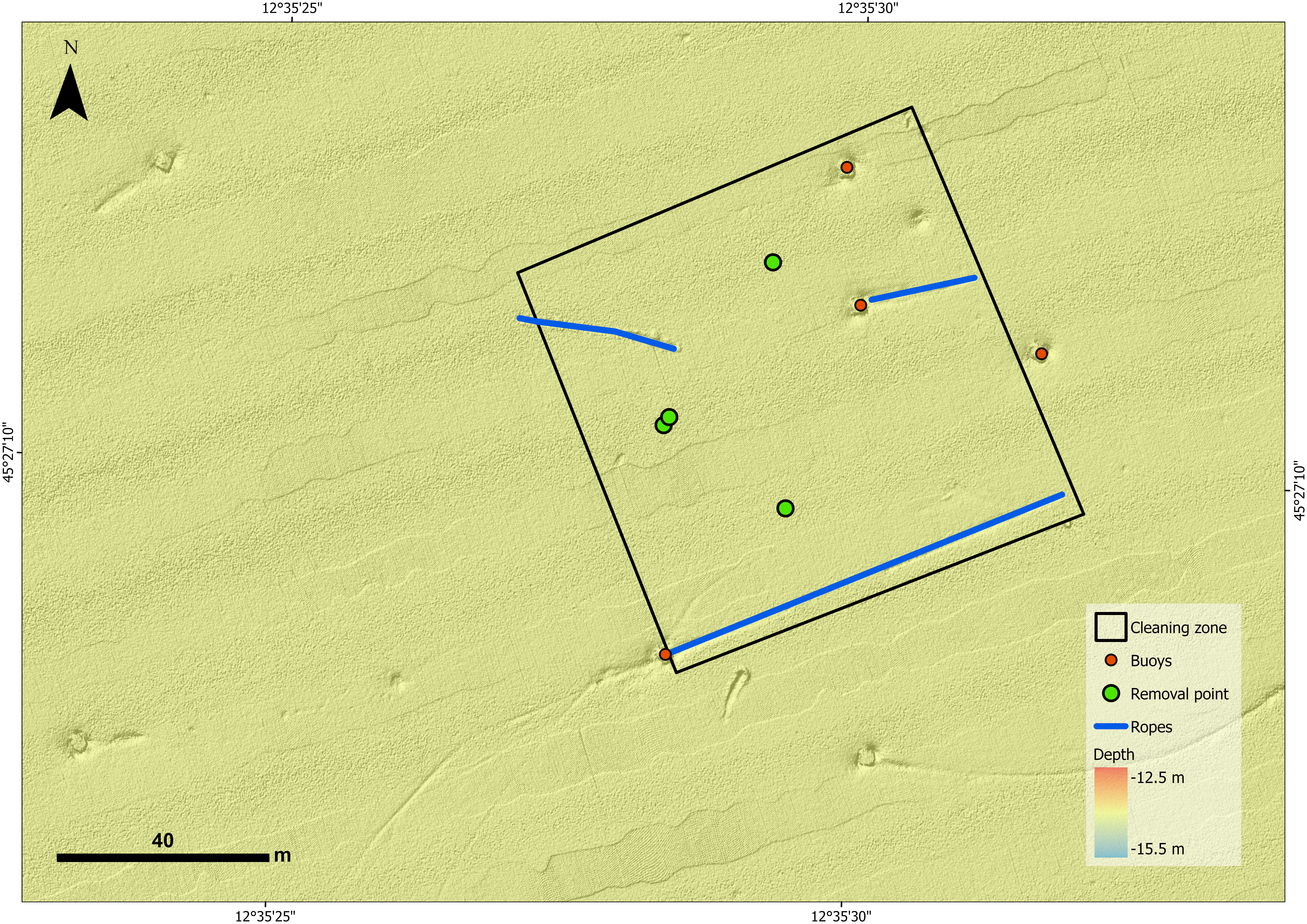
For this project, two study areas were selected and both are characterized by the presence of marine litter that has accumulated over time: a lagoon area (Sacca Fisola) and a coastal area, the latter located on an abandoned mussel farm. The abandoned mussel farm is situated across of the mouth of the river Sile, about 1.7 nautical miles from the coast. It covers a total area of 1960000 sqm with an average depth of 14 m. Mussel farm encloses a sub area called Experimental Field, used in the past for research activities. The examination of bathymetric data facilitated the acquisition of a precise estimation regarding the presence of objects suspended within the water column and resting on the seabed. This evaluation uncovered valuable insights into the underwater conditions and object types, thus enhancing our comprehension of the marine environment in the regions examined.
-
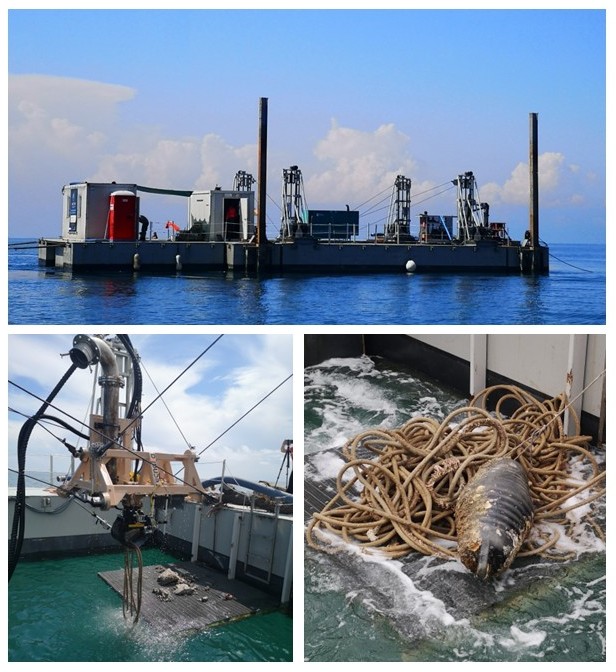

MAELSTROM (Smart Technology for Marine Litter Sustainable Removal and Management) is a Horizon 2020 (H2020) project co-funded by the European Commission, bringing together 14 partners, including research centers, recycling companies, marine scientists, and robotics experts, from eight European countries. The project seeks to reduce the environmental impact of marine litter (ML) on coastal ecosystems by identifying accumulation hotspots, intercepting floating river waste, and removing plastic-based debris from the seabed to prevent its breakdown into microplastics (MPs). At the core of MAELSTROM’s innovative solution is an advanced robotic seabed cleaning platform, developed collaboratively by TECNALIA, CNRS-LIRMM, and "Servizi Tecnici." This floating structure serves as a base station for the cleaning robot, deploying it via cables and winches while integrating a sophisticated suite of underwater sensors to detect, identify, and manage marine litter. The platform supports two key tools: a dredge for collecting smaller debris and a gripper for retrieving larger items, such as tires, boat fragments, and fishing nets. Designed to function as an adaptable and sustainable system, this platform exemplifies cutting-edge technology for marine litter removal and management.
-
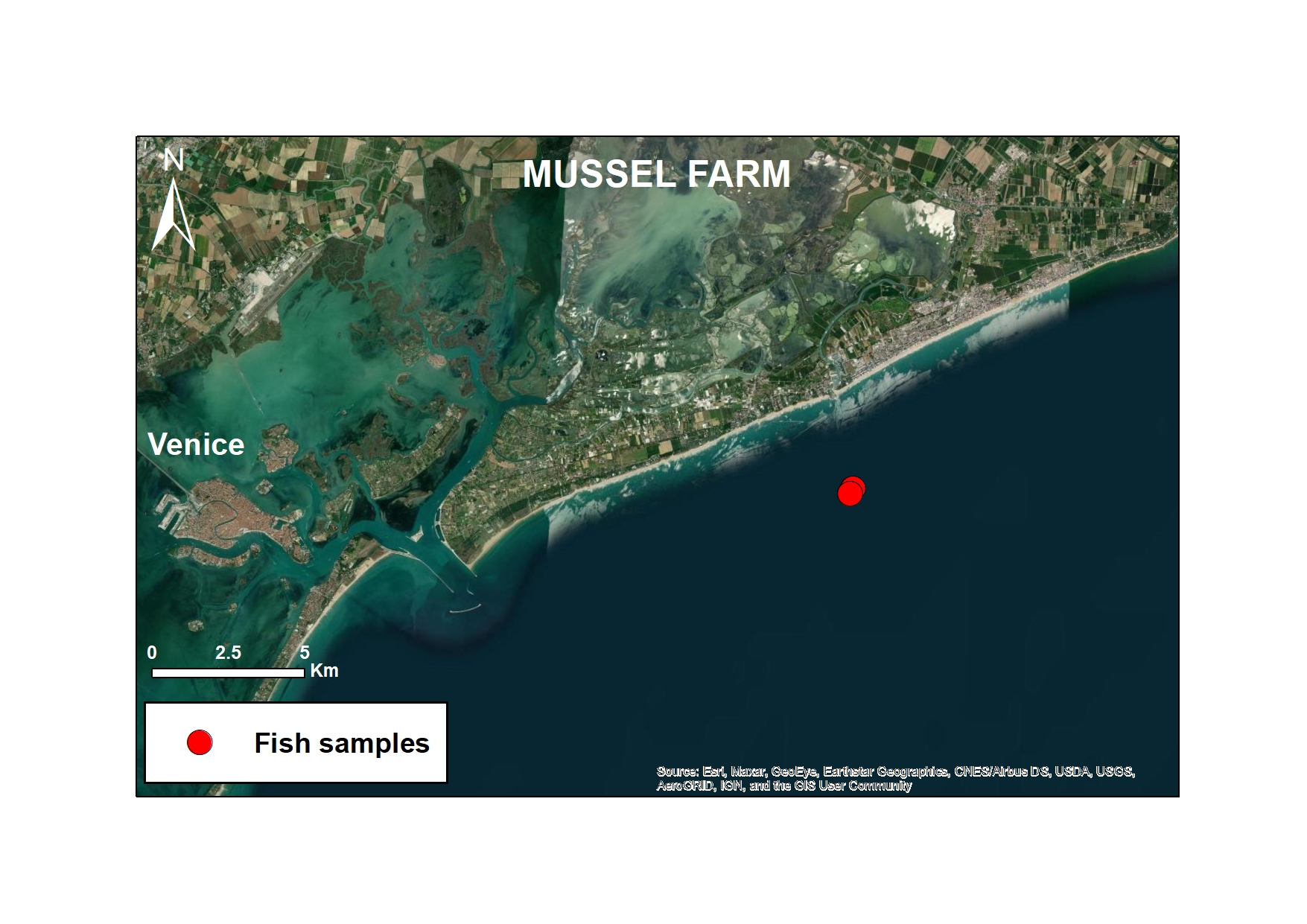
As part of the European MAELSTROM project, microplastic monitoring was carried out to assess the impact of marine cleaning operations. The study focused on two representative sites: Sacca Fisola, within the Venice Lagoon, characterised by high maritime traffic, and Mussel Farm, a coastal area near Cavallino-Jesolo, a former mussel farm. Both sites were monitored every six months and divided into before and after cleaning activities performed by the Seabed Robotic Cleaning Platform (autumn 2022 and spring 2023 for the Sacca Fisola site and spring 2023 for the Mussel Farm site). This innovative robotic system has been designed to remove macro-litter from the seabed. Among the different matrices analysed, particular attention was paid to the biota, with the study of fish species representative of the North Adriatic area, both lagoon and coastal. The species analysed included mullet (Liza sp.), sea bream (Sparus aurata), spiny dogfish (Squalus acanthias) and sole (Solea solea). The main objective was to assess whether the removal of macro plastics from the seabed by the robot was correlated with a reduction in microplastics in the fish themselves, thus contributing to an understanding of the effectiveness of cleaning operations not only on visible debris, but also on the microscopic particles that can be accidentally ingested by these organisms.
 CNR-ISMAR
CNR-ISMAR